Construction of an Oil Seal
The main lip is the most critical component of the seal.
Its sealing edge comes in full contact with the shaft surface in order to provide excellent sealing performance.
(See Figure 3.)
As the pressure increases, the radial load and the friction of the sealing lip increase in contact with the shaft. As with temperature, each oil seal has a recommended pressure for optimum performance. Excessive pressure causes the seals to wear more quickly and consequently have a shorter life.

Rotary Wheel Of Auto Parts
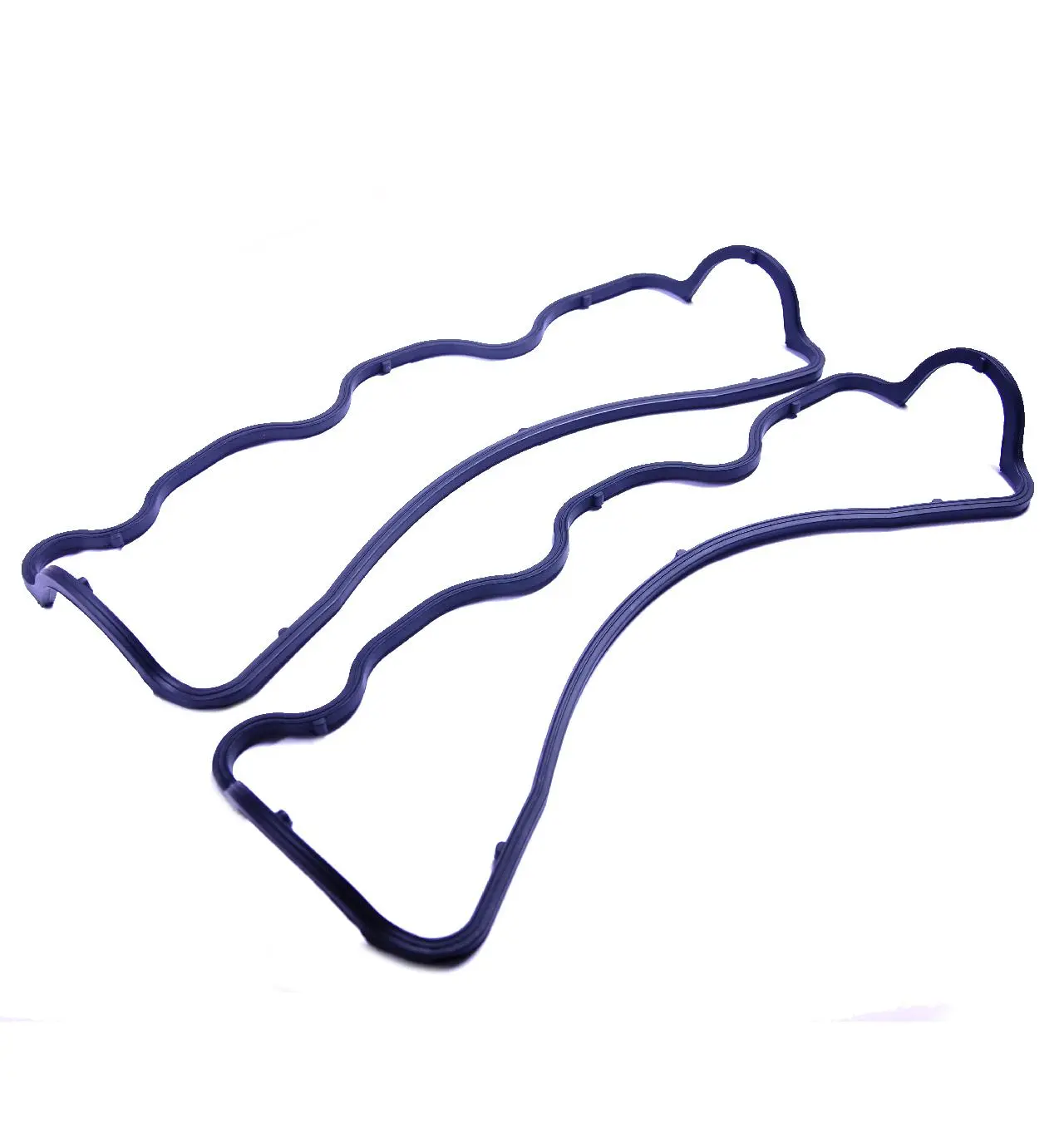
Figure 2: Typically shaped oil seal and component nomenclature
Lay out the pieces of the new gasket on clean newspaper, and note how the joints fit.
 These leaks can lead to oil loss, engine damage, reduced efficiency, and even complete engine failure if left unchecked These leaks can lead to oil loss, engine damage, reduced efficiency, and even complete engine failure if left unchecked
These leaks can lead to oil loss, engine damage, reduced efficiency, and even complete engine failure if left unchecked These leaks can lead to oil loss, engine damage, reduced efficiency, and even complete engine failure if left unchecked rear valve cover gasket. Therefore, regular inspection and timely replacement of the gasket are vital aspects of engine maintenance.
rear valve cover gasket. Therefore, regular inspection and timely replacement of the gasket are vital aspects of engine maintenance.
Choosing the correct type for your application
If it was stuck to the cover, smear gasket sealant along the cover flange and upper gasket and leave it to dry for a few minutes.
When it comes to maintaining the performance of your vehicle, one of the most important components to consider is the spark plug. The spark plug plays a crucial role in igniting the air-fuel mixture in your engine's combustion chamber, which in turn powers your vehicle. Among the various brands and types of spark plugs available in the market, Mico spark plugs are known for their quality and reliability.

Table 5: The major special seals, their shapes, and their features
Figure 1: Types of sealing devices
The lip is specially designed to ensure the oil seal works effectively with the different forces that arise during rotation. Many different designs and materials are used, so countless types of oil seals are available. These are chosen according to the application; pumps, gearboxes, wheels, and many other rotating applications where fluids need to be sealed. They are used in a variety of sectors, such as the chemical industry, manufacturing, wind turbines, automotive sector, food industry, and more. Oil seals are used in nearly all sectors.
PTFE Oil Seals - A relatively new and exciting oil seal, the use of polytetrafluoroethylene means that they can withstand dry or unlubricated operations. With a massive thermal range of -130ºC to +200ºC and a strong resistance to chemicals, they are considered to be the future of rotary shaft seals.
